Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
Introduction Determining how genes function together
2019-10-17
Introduction Determining how genes function together as biological systems is a defining challenge of the genomic era. While genome sequences reveal the DNA blueprint of organisms, deciphering how this blueprint leads to biological function is challenging due in large part to the complexity of prot
-
buy letrozole br Other factors regulating DNA PKcs Recent wo
2019-10-17
Other factors regulating DNA-PKcs Recent work in the field has also focused on factors that regulate NHEJ and NHEJ factors, in particular proteins that modulate DNA-PKcs. In this section we will highlight a number of factors which have been found to regulate DNA-PKcs. DNA-PKcs phosphorylation at
-
As part of a program to
2019-10-17
As part of a program to explore the key binding interactions between the core of 1 and DGAT-1 a systematic analysis of the aminopyrimidine subunit was initiated. A potential approach to improving passive permeability within this series would be to increase lipophilicity via incorporation of substitu
-
Introduction Quassinoids are natural products
2019-10-17
Introduction Quassinoids are natural products formed through the oxidative degradation of triterpene derivatives with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antineoplastic, and antiplasmodial effects (Chakraborty and Pal, 2013; Houël et al., 2013). They are characteristic ingredients of the family Simar
-
The proposed FDIR technique is presented in
2019-10-17
The proposed FDIR technique is presented in the following format: Section 2 contains a survey of typical orbits of interest with regard to the pexidartinib environment found in them, which is contrasted with a LEO orbit. Additionally, how the requirements for the satellite system can be estimated is
-
Recent studies showed that the activity of
2019-10-17
Recent studies showed that the activity of CK2 was significantly reduced in ischemic stroke model rats, and cerebral I/R injury significantly decreased the expression of CK2α (Lee et al., 2004; Kim et al., 2012; Zhou et al., 2016). In addition, the dysregulation of CK2 is involved in ERS/UPR in non-
-
Notably HSP expression is under control of
2019-10-17
Notably, HSP27 expression is under control of the tetrameric form of CK2 holoenzyme, as knockout or knockdown of the β regulatory subunit alone reproduces the same effects of targeting the α/α′ catalytic subunits. This observation discloses the possibility to use more specific drugs that affects onl
-
Since the aggregation of neurotoxic forms of A plays
2019-10-17
Since the aggregation of neurotoxic forms of Aβ plays a pivotal role in AD pathogenesis, an approach that using small molecules to bind Aβ monomers and prevent their assembly into cytotoxic oligomers attracts great interest for the development of AD drugs. Therefore, the potential inhibitory activit
-
Table summarizes the literature data available on the
2019-10-17
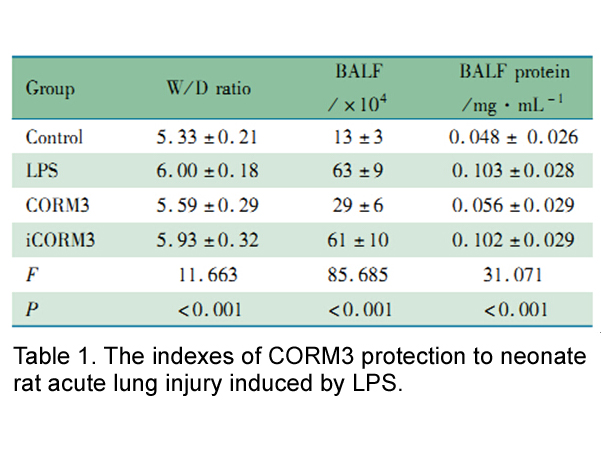
Table 4 summarizes the literature data available on the occurrence of these two dexdomitor of steroidal compounds in sludge and sediments. In activated and digested sewage sludge, the concentrations of ethynyl estradiol (17 ng/g), estrone (37 ng/g ), and estradiol (49 ng/g) found in one of the very
-
Here we report for the
2019-10-17
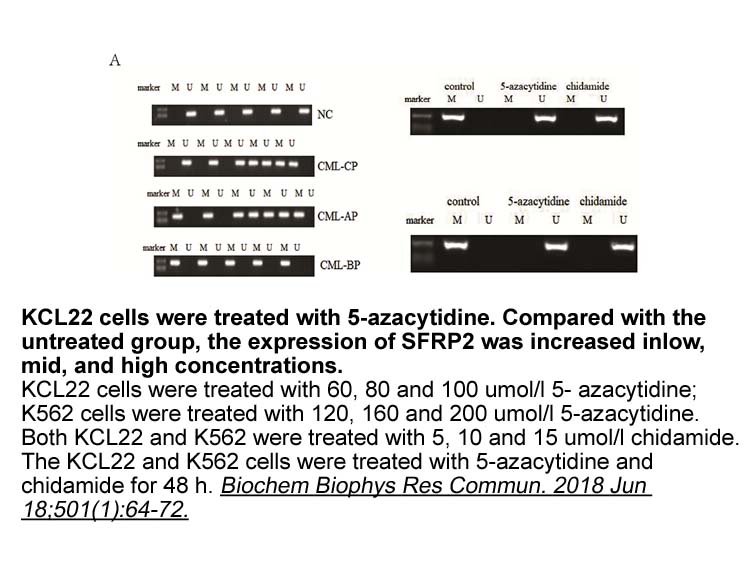
Here, we report for the first time that EphB4 contains two NLS sequences and localises to the nucleus. This is mediated via an importin-α pathway and we show that EphB4 could potentially have a direct role in gene regulation. These data provide new insight into Eph receptor localisation and action a
-
To develop novel EPAC inhibitors
2019-10-17
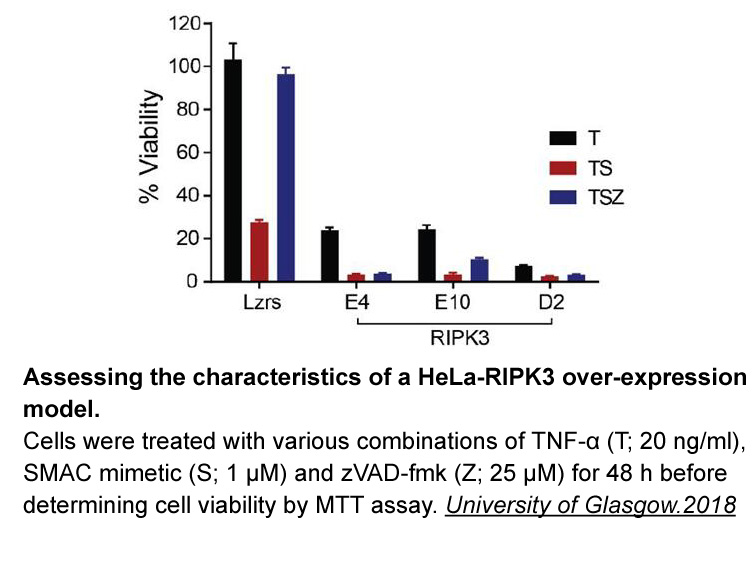
To develop novel EPAC inhibitors, Zhou and co-workers optimized the HTS hit as the chemical lead. After modifications of the substituents on the phenyl ring or C6-position of compound , compound () was identified to be the more potent compound in this series with an IC value of 4.0µM (EPAC2). Dock
-
The assembly and maturation of invadopodia
2019-10-16
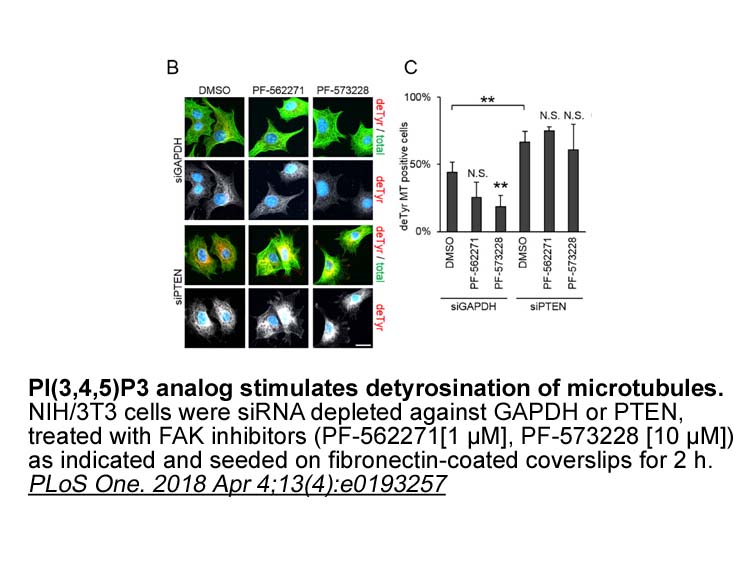
The assembly and maturation of invadopodia can be initiated by chemical stimuli such as the epidermal growth factor (EGF), as well as the mechanical signals from extracellular matrix (ECM). Upon binding, EGF activates the EGF receptor (EGFR), which further activates several intracellular signaling p
-
An important role for the precursor molecule of the
2019-10-16
An important role for the precursor molecule of the main EBI2 ligand, 25-OHC, in the inhibition of inflammation was recently shown. 25-OHC was demonstrated to inhibit inflammasome induction in mouse macrophages [28]. Inflammasome assemblies are the sites of caspase 1 activation and lead to the gener
-
Each of these substrate receptors
2019-10-16
Each of these substrate receptors belongs to a multigene family with tens, if not hundreds of members in plants, and with in part overlapping and in part differential substrate specificities [4]. The complexity of the system is nicely illustrated by the F-box protein and auxin receptor TRANSPORT INH
-
SB 204070 mass In this study using REMD
2019-10-16
In this study, using REMD with the crystal environment, we investigate the effect of cryo-cooling on the crystal structure of Escherichia coli DHFR. DHFR is an important model enzyme (for review, see, e.g., (30)), and has been studied for decades (31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43).
14808 records 945/988 page Previous Next First page 上5页 941942943944945 下5页 Last page